author of Honorable Influence - founder of Mindful Marketing
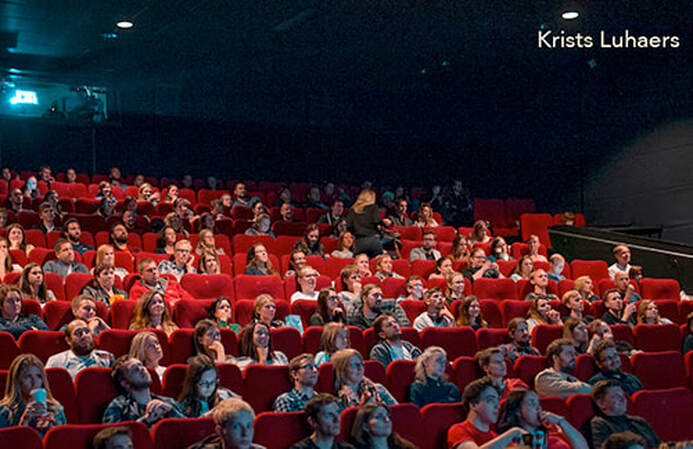
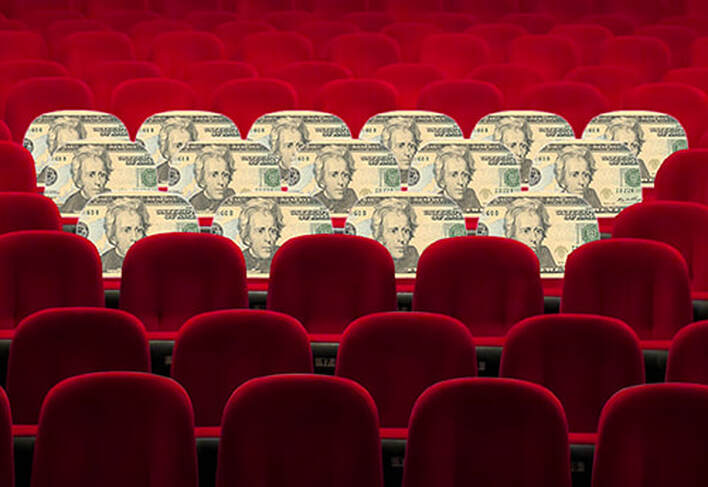
Many moviegoers are likely giving a two-thumbs-down rating to AMC Entertainment, the world’s largest cinema chain, for its recent announcement that it will charge higher prices for more sought-after middle-of-theater seats.
It’s natural for anyone who pays their own hard-earned money for things to dislike price increases, especially when there seems to be no reason beyond a business’s realization, “We can charge for that.”
Movie theaters, however, have endured very hard times over the past decade. First, streaming services and home entertainment centers lured away from theaters many who realized they could enjoy a cinematic experience in the comfort of their own homes. The pandemic’s quarantines and social distancing exasperated that trend. Most recently, inflation has caused many consumers to monitor more carefully their discretionary spending.
To call these events “challenges” is like calling Tom Hanks “some actor.” Rather, they’ve been existential threats, as Cineworld unfortunately knows. Last September, the world’s second largest movie theater chain and owner of Regal Cinemas, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy.
Maybe premium-priced seating is something movie theaters must do to stay solvent. In many other industries, such variable pricing is a staple of their revenue streams:
- Live theatre, concerts, and sporting events have long charged more for better seats.
- All kinds of service providers, from car washes to hair salons, demand more for higher levels of service.
- Many goods producers charge more for their premium products and more sought-after brands, for instance, automakers are well-known for various trim levels (DX, LX, ELX, etc.) and some, like Toyota, offer higher-end vehicles under a different brand, e.g., Lexus.
Ultimately, most product pricing decisions come down to supply and demand. Whether they’re from Gap or Gucci, products that are in greater demand tend to cost more. As price rises, quantity demanded decreases, helping ensure that supply can keep pace.
In free markets, businesses decide what they want to sell, and consumers choose what they want to purchase. No one has to go to a movie theater or when there, purchase a premium seat. It’s their choice to do those things, which makes it hard to argue that AMC is in any way acting unfairly.
So, charging more for certain cinema seats probably isn’t unethical, but is it really an effective business strategy?
A main problem with the premium approach is likely consumers’ perceptions ingrained from years of cinematic experience. For more than a century, moviegoers have freely chosen their theater seats, including those in the center. It’s hard to suddenly start charging for something that people have been getting for free, especially when an upcharge seems unwarranted.
In contrast, the seats in the very front of the theater seem like they should cost less. In fact, why do theaters even have those close-up seats that few people choose and that have been mocked in sitcoms like Seinfeld. Of course, theaters need to cover substantial retail space leases and other expenses, which means fitting in as many paying patrons as possible. However, to demand the same admission price for such suboptimal seating is a big ask.
Here’s what movie theaters should consider instead:
- Raise ticket prices slightly, across the board: Again, no one likes price increases, but people who want a true cinema experience can tolerate a modest increase. Moreover, they can understand the need to do so, given the unique pressures theaters have been under, outlined above, and because they see many other organizations doing the same.
- Discount the close-up seats: As just mentioned, these seats are significantly less valuable than any others in the theater. Other events often offer discounts on seats with obstructed views, etc. Movie theaters could do the same, or they could get creative and give patrons who sit in those seats something extra like a coupon for a free small soft drink or a popcorn-size upgrade. Consumers may even perceive such incentives as more valuable than a small ticket price discount, and the freebies could be less costly to the theater companies.
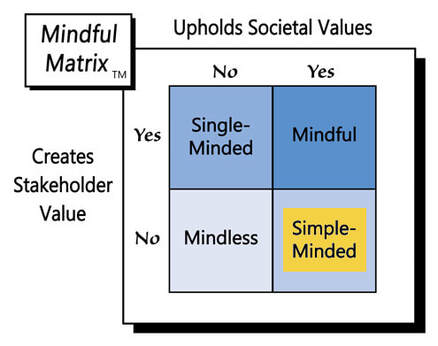
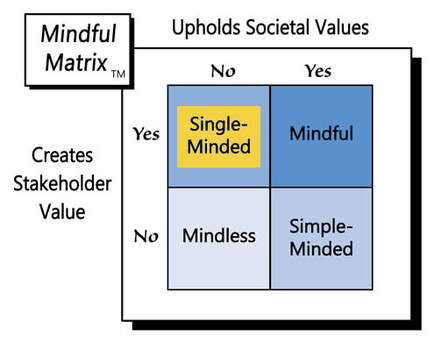
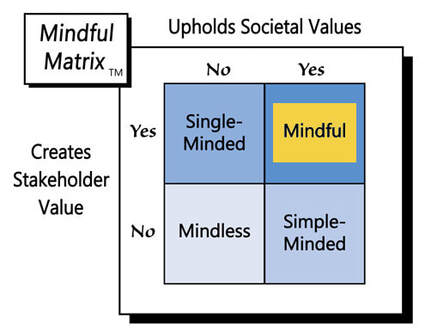
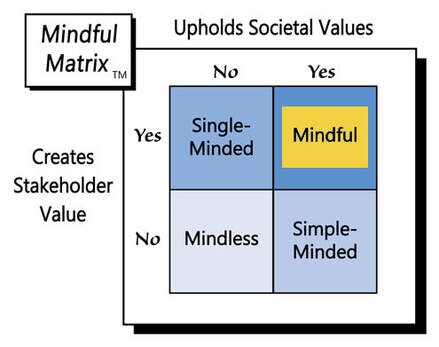
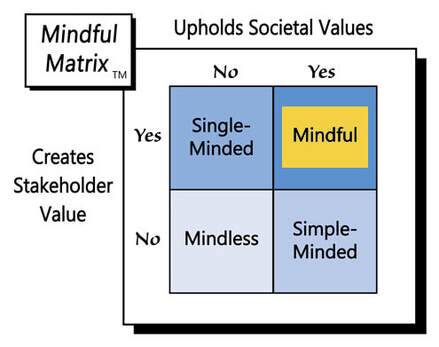
In a free market, it’s not inherently unethical for AMC or other movie theater chains to charge more for choice seating, but such a strategy probably won’t sit well with consumers, who have chosen those middle seats for free for so long. For that reason, the ending of this cinematic story will likely be “Simple-Minded Marketing.”
Learn more about the Mindful Matrix.
Check out Mindful Marketing Ads and Vote your Mind!
























 RSS Feed
RSS Feed